The Malaysian Flying Car Project is actually a Chinese Drone
Back in February, we wrote an article explaining our thoughts on the Malaysian Flying Car Project. In essence, we thought the project had some potential but seemed improbable with its RM1,000,000 R&D funding. Well this week, the topic was brought up again in Dewan Rakyat and here are the latest developments:
- A local test flight will be carried out tomorrow
- It is essentially a Chinese made drone with a capacity for 2 human passengers
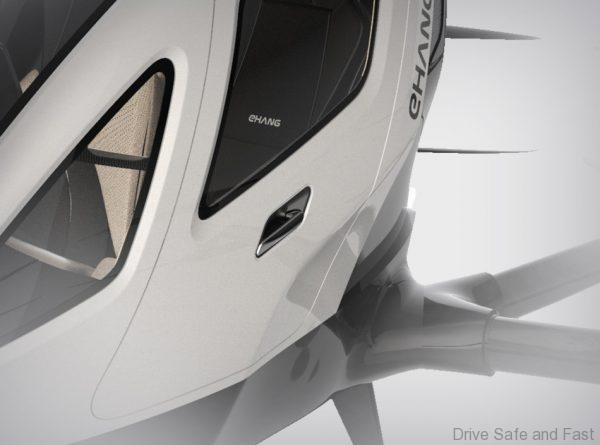
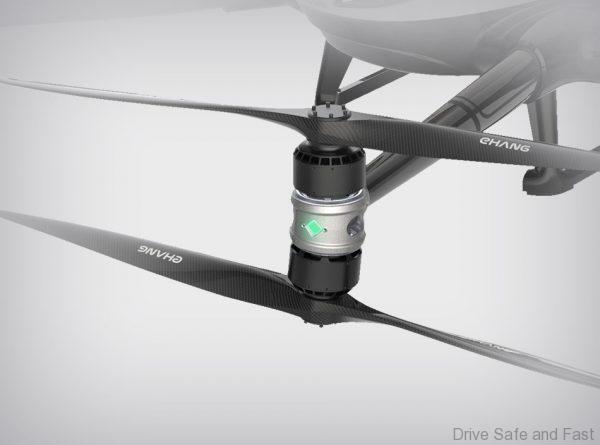
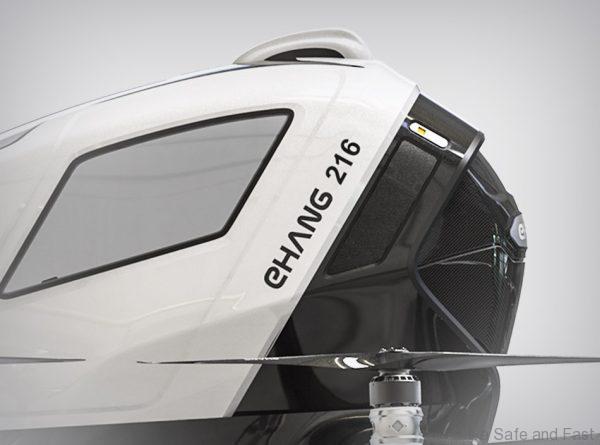
- The drone in question is an Ehang 216 (specs below)
- Transport Minister YB Anthony Loke stated that it is a drone, and not a ‘car’
- Entrepreneur and Development Minister DS Mohd Redzuan Yusof stated that there isn’t a substantial difference
- The government has injected no money into the project.
We tend to agree with both ministers. Perhaps calling it a flying car was the wrong idea, but it’s certainly more than just an unmanned drone. The vehicle in question is able to fly for 25 minutes and cover 30-40 km in that time. It can also seat 2, as the unrelated prototype that shown earlier did.
But we also have to call out Dato Seri Mohd Redzuan Yusof for previously stating that the drone would be fully driven by local technology. We know now that the vehicle will merely be assembled here, with most of the engineering and testing work already done in China by Beijing Yi-Hang Creation Science & Technology Co., Ltd. This wasn’t what was promised.

While we still think something like this could have practical applications in densely populated cities, it appears a more immediate use for these aircraft is in the palm oil industry, where large swathes of crops can be effectively sprayed.
Ehang 216 Specs and details from Wikipedia:
“The 216 is a two-seater with 16 propellers in a coaxial double-baled design. It has made over 1,000 manned flights by July 2018 and its maximum range flown was 8.8 km (5.5 miles). It can fly 25 min for a range of 30–40 km (16–22 nmi). The aircraft is targeted for autonomous flying, to be monitored from an Ehang or its customer command-and-control center. Austrian aerostructures supplier FACC AG partnered with Ehang to certify and produce the aircraft in Europe, within simpler certification requirements for takeoff weights below 600 kg (1,320 lb).
In October 2018, the CAAC approved initial passenger operations at specific locations to develop urban air taxis regulations. Ehang began taking preorders since, for island-hopping and to a Chinese coastal resort for aerial sightseeing within their site. A 1 km (0.54 nmi) shuttle across the river of its home city of Guangzhou should avoid a 30 min drive due to traffic congestion on the downtown bridge. US biotechnology company United Therapeutics, manufacturing organs for human transplants, should test rapid automated delivery from laboratory to hospital by the end of 2019.
Specifications
General characteristics
- Crew: None (self-piloted)
- Capacity: 2 passengers 260kg
- Length: 5.61 m (18 ft 5 in)
- Height: 1.76 m (5 ft 9 in)
- Propellers: 16-bladed
Performance
- Maximum speed: 160 km/h (99 mph, 86 kn)
- Cruise speed: 130 km/h (81 mph, 70 kn)
- Minimum control speed: 70 km/h (43 mph, 38 kn)
- Range: 16 km (9.9 mi, 8.6 nmi)”